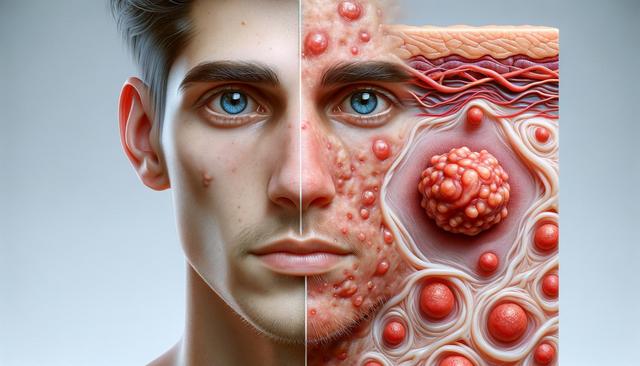
What Are Warts and Why Do They Appear?
Warts are small, rough skin growths caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). They often appear on hands, feet, or other parts of the body and can spread through direct contact or shared surfaces. The virus enters the skin through small cuts or abrasions, especially in moist environments like gyms or shared showers. Children and individuals with weakened immune systems are generally more susceptible. Although warts are typically harmless, they can be uncomfortable and cosmetically undesirable, prompting many to seek removal solutions. It’s important to note that not all skin growths are warts, so a healthcare provider’s diagnosis can be helpful before beginning treatment.
Common Types of Warts
Warts come in several types, each with distinct characteristics. Understanding the type of wart can help determine the most appropriate removal method. The most frequently encountered varieties include:
- Common warts: Typically found on fingers and hands, they have a rough, raised surface.
- Plantar warts: Develop on the soles of the feet and may feel like stepping on a pebble due to their inward growth.
- Flat warts: Smaller and smoother, often appearing in clusters on the face, thighs, or arms.
- Filiform warts: Long and narrow, usually growing around the mouth, nose, or eyes.
- Periungual warts: Appear around fingernails and toenails, potentially affecting nail growth.
Each type may respond differently to treatment, and in some cases, professional evaluation is necessary to distinguish them from other skin conditions.
Over-the-Counter and Home Remedies
Many people begin wart removal with over-the-counter (OTC) options or home remedies. These approaches can be effective for common and minor warts, though they may require patience and consistent use. Some widely used methods include:
- Salicylic acid: Available in various forms like gels, pads, or liquids, this compound helps peel away infected skin layers.
- Freezing sprays: Mimicking cryotherapy, these products use cold temperatures to destroy wart tissue.
- Duct tape: Though evidence is mixed, some find success using duct tape to cover the wart and peel it off gradually.
- Natural options: Remedies such as tea tree oil, apple cider vinegar, or garlic are popular, though their effectiveness is largely anecdotal.
While home treatments can be helpful, they are not guaranteed to work for every individual or wart type. If there’s no improvement after several weeks, considering a professional option may be the next step.
Professional Wart Removal Methods
When over-the-counter solutions don’t yield results, professional wart removal procedures may offer a more targeted and effective approach. Medical providers can evaluate the wart’s type and location to recommend a suitable treatment. Common clinical methods include:
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, causing it to blister and fall off over time.
- Laser treatment: Utilizing focused light to destroy wart tissue, typically reserved for stubborn or recurring warts.
- Electrosurgery and curettage: Burning the wart and scraping it off under local anesthesia.
- Prescription creams: Certain topical treatments may stimulate the immune system to fight off the virus.
These procedures are generally safe but may require multiple sessions or have minor side effects like discomfort or scarring. Discussing options thoroughly with a dermatologist can help set realistic expectations based on individual skin type and health status.
Aftercare and Preventing Recurrence
Effective wart removal doesn’t end with treatment—aftercare and prevention play a crucial role in ensuring the wart doesn’t return or spread. Post-treatment, it’s important to follow any care instructions provided by a healthcare provider to support healing. Key aftercare tips include:
- Keeping the area clean and dry to prevent infection.
- Avoiding picking at the site, which can cause scarring or viral spread.
- Using bandages if needed to protect sensitive skin during recovery.
Preventing future warts involves minimizing contact with the virus. Practical strategies include:
- Wearing flip-flops in communal showers or pools.
- Avoiding direct contact with warts—yours or others’.
- Not sharing personal items like towels or razors.
- Maintaining healthy skin by moisturizing and treating cuts promptly.
Good hygiene and immune system support are essential in reducing the likelihood of new wart formation, especially for those prone to recurrence.
Conclusion: Taking the Right Steps Toward Wart-Free Skin
Wart removal can be a gradual process, and the right approach often depends on the type of wart, its location, and individual health factors. From home remedies to professional treatments, there are multiple options to explore. Understanding the causes, identifying the wart type, and selecting appropriate care methods are key to effective removal and prevention. Whether you’re dealing with a minor issue or a persistent case, taking informed and consistent steps can help you manage warts and maintain healthy skin.