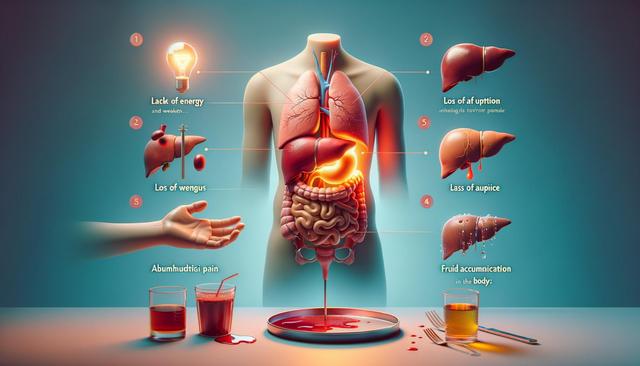
Chronic Fatigue and Weakness
One of the early and most common symptoms of liver cirrhosis is persistent fatigue. Individuals may feel constantly tired, even after a full night’s sleep or periods of rest. This overwhelming exhaustion is not just physical but can also include mental fatigue, making daily tasks feel burdensome. Fatigue in liver cirrhosis is often caused by the liver’s reduced ability to filter toxins and produce energy-efficiently, which affects the entire body.
Fatigue may worsen as the disease progresses, which often impacts quality of life. Managing this symptom involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Patients are typically advised to:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients
- Limit alcohol and processed foods
- Get regular but gentle exercise like walking or yoga
- Use medications prescribed by healthcare providers to manage underlying causes
Fatigue should always be discussed with a healthcare professional, as it may also signal complications that need immediate attention.
Jaundice (Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes)
Jaundice is a hallmark sign of liver dysfunction, including cirrhosis. It occurs when the liver cannot effectively process bilirubin, a yellow pigment formed from the breakdown of red blood cells. As bilirubin accumulates in the bloodstream, it causes a yellowish tint to the skin and the whites of the eyes.
This symptom is a clear indication of significant liver impairment and often prompts individuals to seek medical evaluation. Additional signs associated with jaundice may include:
- Dark-colored urine
- Pale stools
- Itchy skin
Treatment of jaundice in liver cirrhosis focuses on managing the underlying liver condition. In some cases, medications may be used to improve liver function or reduce bilirubin levels. Routine monitoring and liver function tests are essential to track progression and response to treatment.
Abdominal Pain and Swelling
Another significant symptom of liver cirrhosis is abdominal discomfort, particularly in the upper right side, where the liver is located. As cirrhosis advances, it may lead to ascites, a condition involving the buildup of fluid in the abdomen. This can cause noticeable swelling, bloating, and a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the belly area.
Patients experiencing abdominal pain or swelling should be evaluated promptly, as untreated ascites can lead to further complications, such as infection or respiratory difficulties due to pressure on the diaphragm.
Management strategies include:
- Limiting sodium intake to reduce fluid retention
- Using diuretics under medical supervision
- Paracentesis, a procedure to remove excess abdominal fluid
- Medications to manage portal hypertension, a common cause of ascites
Monitoring abdominal symptoms closely and following up regularly with a healthcare provider is essential for effective management.
Easy Bruising and Bleeding
The liver plays a vital role in producing proteins necessary for blood clotting. In cirrhosis, diminished liver function can lead to reduced production of these clotting factors, resulting in easy bruising and prolonged bleeding. Individuals may notice that minor bumps cause significant bruises, or that cuts take longer to stop bleeding.
This symptom can be particularly concerning if internal bleeding occurs, which may not be immediately visible. Signs of internal bleeding can include:
- Black or tarry stools
- Blood in vomit or coughing up blood
- Unexplained drop in blood pressure or dizziness
To manage this symptom, doctors may recommend blood tests to monitor clotting ability, vitamin K supplements, and in severe cases, transfusions. Avoiding medications that affect blood clotting, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), is also advised. Early detection and intervention are crucial to mitigate risks.
Confusion or Cognitive Changes (Hepatic Encephalopathy)
Hepatic encephalopathy is a serious condition associated with advanced liver cirrhosis. It occurs when the liver fails to remove toxins from the blood, which then reach the brain and affect mental function. Symptoms range from mild confusion and forgetfulness to severe disorientation and even coma in advanced cases.
Early signs often include:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Changes in sleep patterns
- Slurred speech
- Unusual behavior or mood swings
Hepatic encephalopathy requires immediate medical attention. Treatment typically involves medications that reduce toxin levels, such as lactulose and certain antibiotics. Dietary adjustments, including reduced protein intake, may also help manage symptoms. Patients and caregivers should be educated to recognize early warning signs to ensure timely intervention.
Conclusion: Recognizing and Managing Liver Cirrhosis Symptoms
Liver cirrhosis is a progressive condition that can significantly impact various aspects of health, but early recognition of symptoms such as fatigue, jaundice, abdominal swelling, easy bruising, and cognitive changes can improve outcomes. By understanding these warning signs and seeking prompt medical care, individuals can take proactive steps toward effective management.
Treatment plans vary depending on the severity of the condition, but may include lifestyle changes, medications to support liver function, and monitoring for complications. Working closely with healthcare providers and staying informed about the condition are essential to slowing progression and maintaining a better quality of life.